Energy Investment Guide
The Energy Investment Guide, prepared by the KSE Institute in partnership with the Ministry of Economy of Ukraine, the Ministry of Energy of Ukraine, and KPMG Ukraine, offers an in-depth analysis of financing programs and investment opportunities in Ukraine’s energy sector. It highlights critical areas such as electricity generation, distribution, and biogas production, providing clear pathways for project financing and collaboration.
The Guide is a valuable resource for potential investors, banking institutions, and project initiators, aiming to foster innovation, sustainability, and economic resilience in the face of post-war recovery challenges.
For those looking to explore Ukraine’s energy sector. Gain insights into financing opportunities, investment potential, and key areas for growth.
Ukraine’s energy sector has faced severe wartime losses, with over 9 GW of capacity destroyed and 18 GW, including Europe’s largest nuclear plant, under occupation. Despite this, Ukraine is driving recovery through extensive repairs and 662 MW of new renewable capacity, supported by domestic and international investments to stabilize energy supply, integrate with European markets, and attract foreign capital for long-term growth.
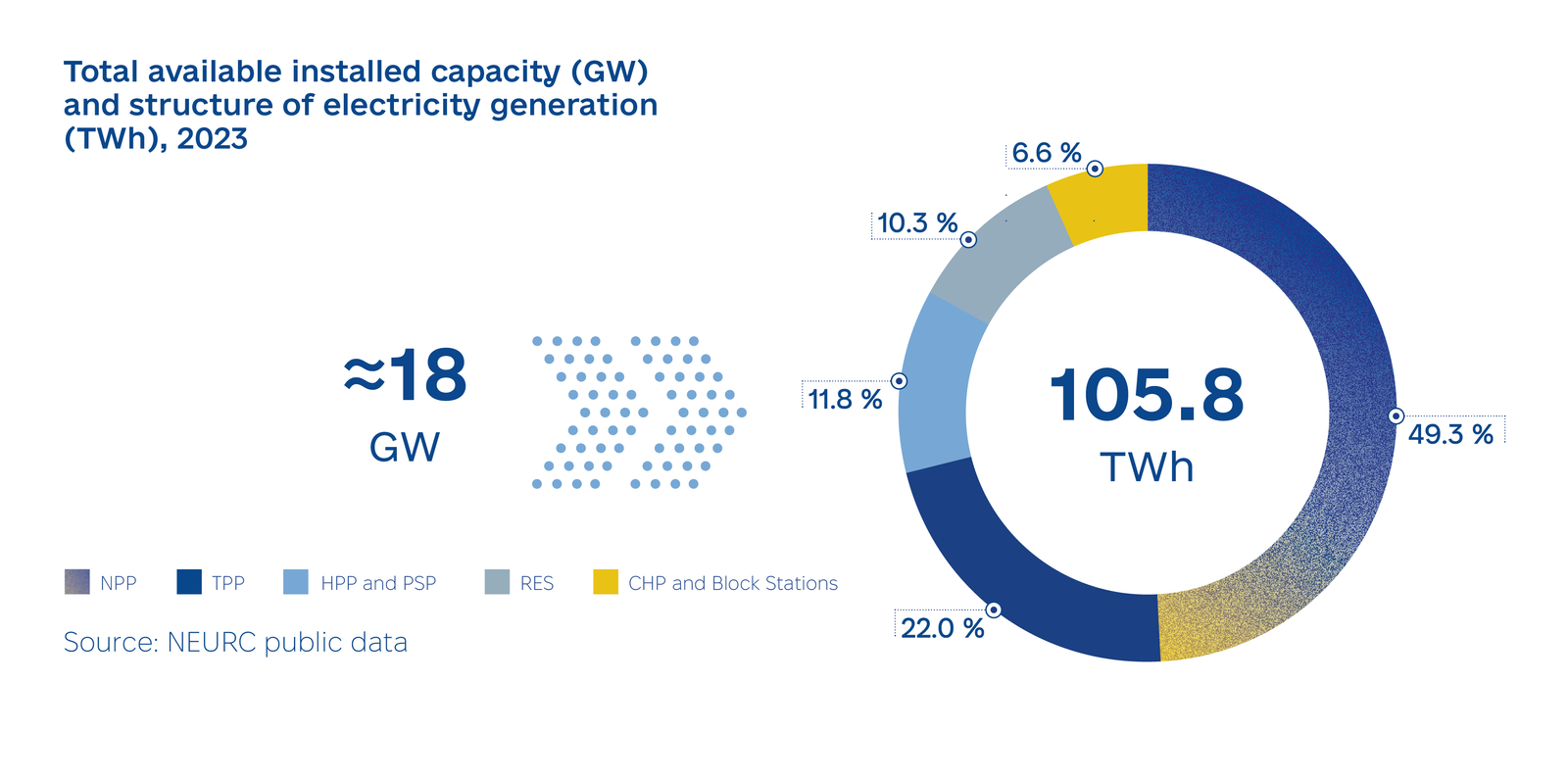
Ukraine’s power system remains resilient amid wartime challenges, with nuclear energy supplying 60% of electricity and stabilizing the grid. Through its “green recovery” strategy, Ukraine plans to add 21.1 GW of renewable capacity by 2030, leveraging its vast 750 GW potential to support Europe’s green transition and energy security.
Current state of the power system
Ukraine’s energy sector has endured severe challenges during the war, with over 9 GW of capacity destroyed and 18 GW, including the Zaporizhzhia NPP, under occupation. The imbalance in electricity supply and demand, driven by a reliance on nuclear and weather-dependent renewable sources, has left the country dependent on ENTSO-E imports and power outages to stabilize consumption. Despite these difficulties, Ukraine is conducting its largest-ever repair campaign and commissioning new facilities, showcasing its determination to restore energy stability amidst conflict.
Recovery efforts are further bolstered by significant investments and international cooperation. Since 2022, 662 MW of renewable capacity has been added, while DTEK and USAID have contributed $300 million and $475 million, respectively, to infrastructure development. Agreements with Siemens Energy, Deutsche Bank, and other global partners secured during URC-2024, alongside $1.3 billion in financial commitments from international allies, underscore the critical role of foreign investment in rebuilding Ukraine’s energy system and driving long-term economic resilience.
Prospects for the development of electricity generation
In 2024, Ukraine’s power system demonstrated remarkable resilience despite ongoing Russian attacks that caused significant damage to infrastructure and capacity losses. Nuclear power generation emerged as the backbone of the system, supplying 60% of the country’s electricity and ensuring stability amid the conflict. At the same time, the government advanced its “green recovery” strategy, emphasizing sustainability, affordability, and the development of distributed generation to enhance energy efficiency and reduce vulnerabilities.
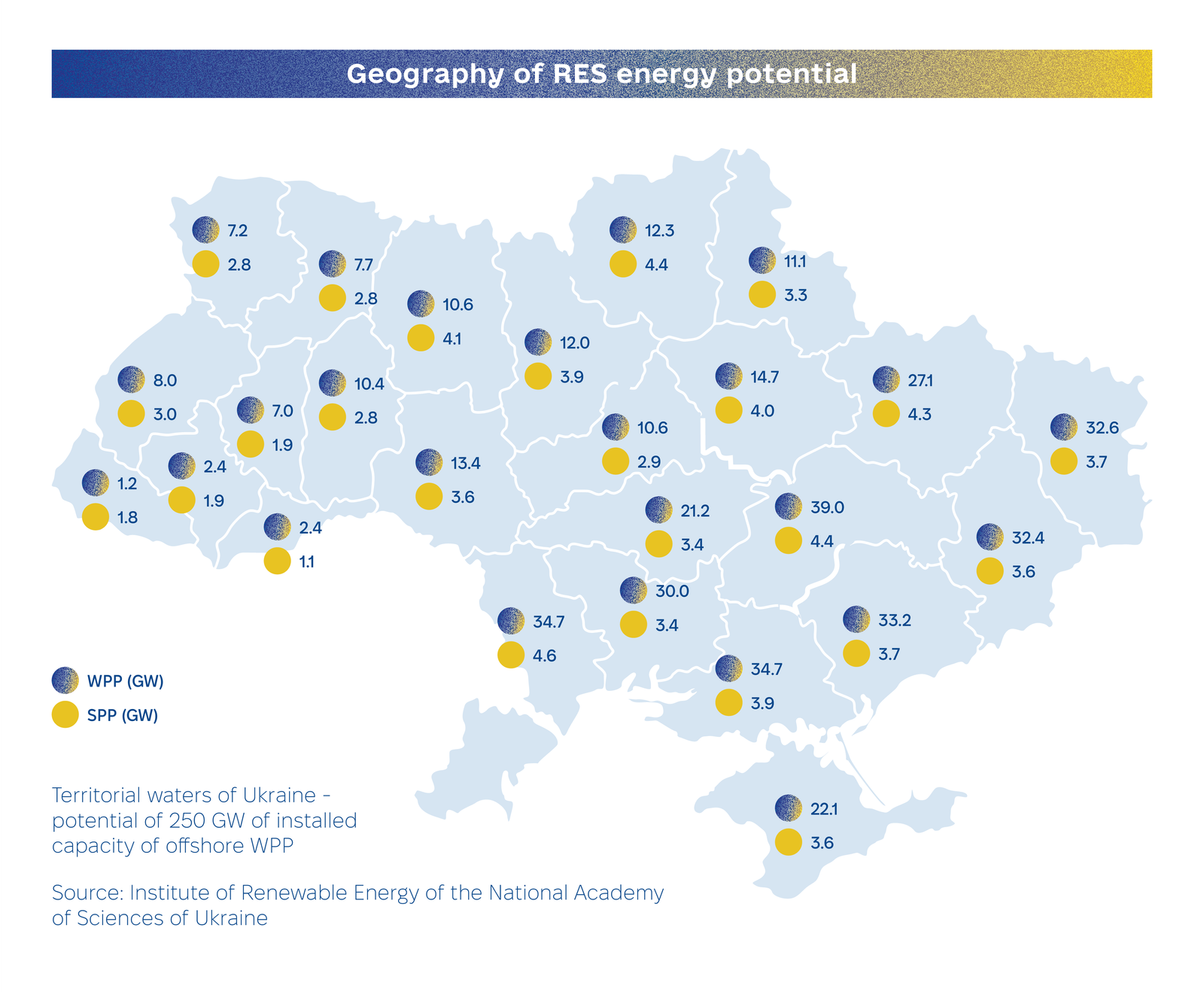
Renewable energy sources (RES) are at the heart of Ukraine’s energy transition, with plans to increase RES capacity by 21.1 GW by 2030 and achieve a 27% contribution to gross energy consumption. Ukraine’s vast RES potential, exceeding 750 GW, positions it as a key partner in the EU’s green transition. With the ability to produce over 2,200 TWh annually — equivalent to 80% of the EU’s electricity consumption — Ukraine is poised to become a major exporter of green energy and hydrogen, contributing to Europe’s decarbonization and the integration of its energy markets.
Ukraine has strengthened its legal framework to attract energy investments and modernize its power sector. Key reforms, including Corporate PPAs, guarantees of origin, and improved “green auctions,” align with EU standards, fostering a competitive market. By advancing distributed generation and addressing challenges like “green tariff” debt, Ukraine is creating a resilient, investor-friendly energy sector poised for European integration and long-term growth.
Ukraine has implemented significant reforms to boost energy investments, including Corporate Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and guarantees of origin for renewable energy, aligning with EU standards. Enhancements to “green auctions,” such as contracts for difference and simplified participation, have created a transparent and competitive environment, with pilot auctions already launched.
The government is advancing distributed generation through tax incentives, streamlined construction and connection procedures, and long-term ancillary service contracts. These measures enhance energy system resilience, reduce reliance on centralized power, and attract private sector participation, as outlined in the Distributed Generation Development Strategy through 2035.
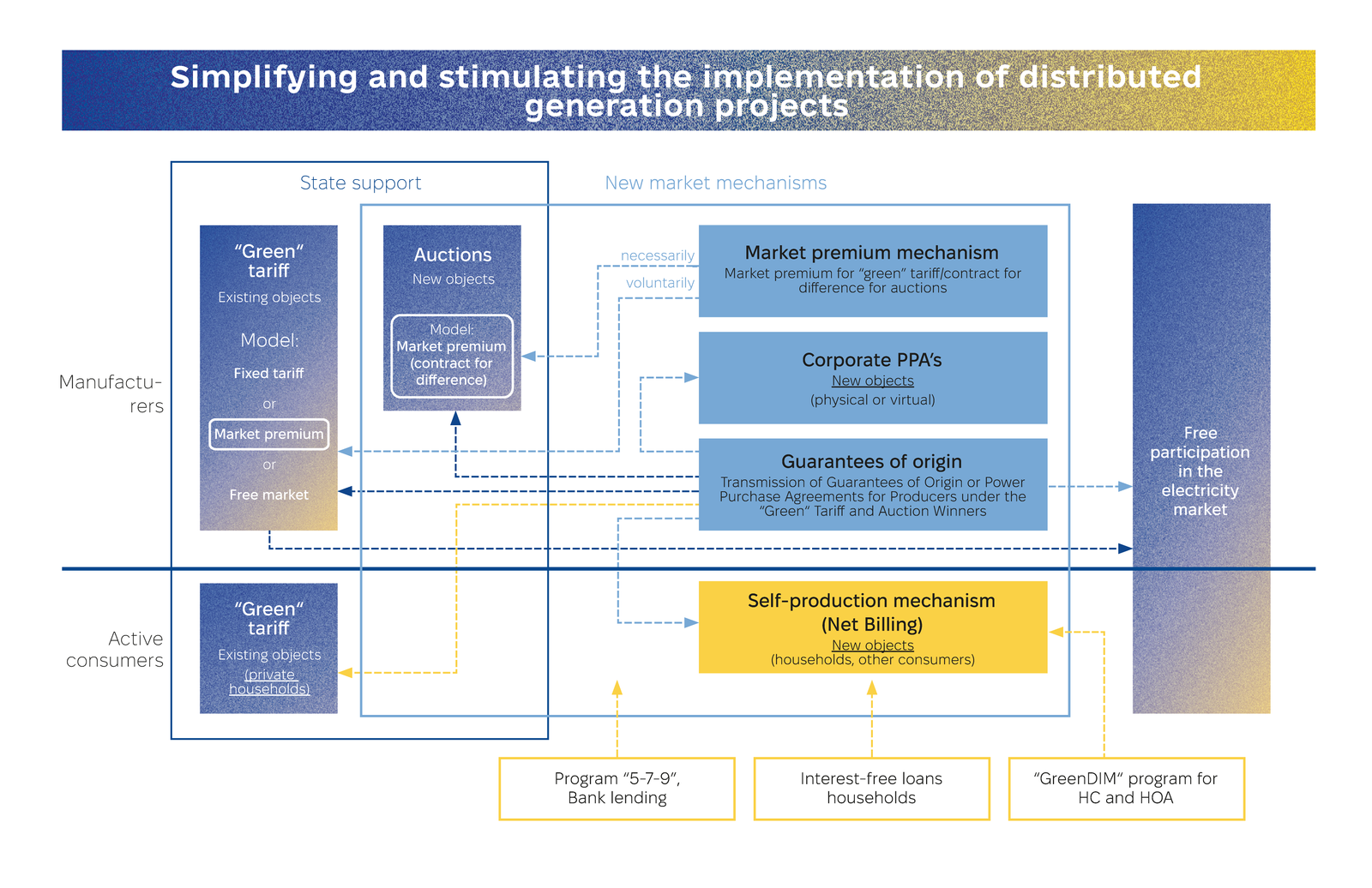
Market integration with the EU is progressing through harmonized regulations, liquidity improvements, and stronger oversight to prevent market abuse. Alongside these efforts, Ukraine is addressing legacy challenges, including “green tariff” debt and payment discipline, positioning itself as a key partner in Europe’s green transition and a compelling destination for energy investments.
Ukraine’s energy sector recovery is being driven by a combination of international and domestic financing programs. Under Phase 1 of the Ukraine Investment Framework (UIF), €1.4 billion is available for energy projects through institutions like the EIB, EBRD, and IFC, with the potential to unlock up to €1.7 billion when combined with domestic programs. Ukrainian banks have also introduced extensive lending initiatives, supported by the National Bank of Ukraine, to finance renewable energy and energy-saving projects, with UAH 11.7 billion in loans already approved by late 2024.
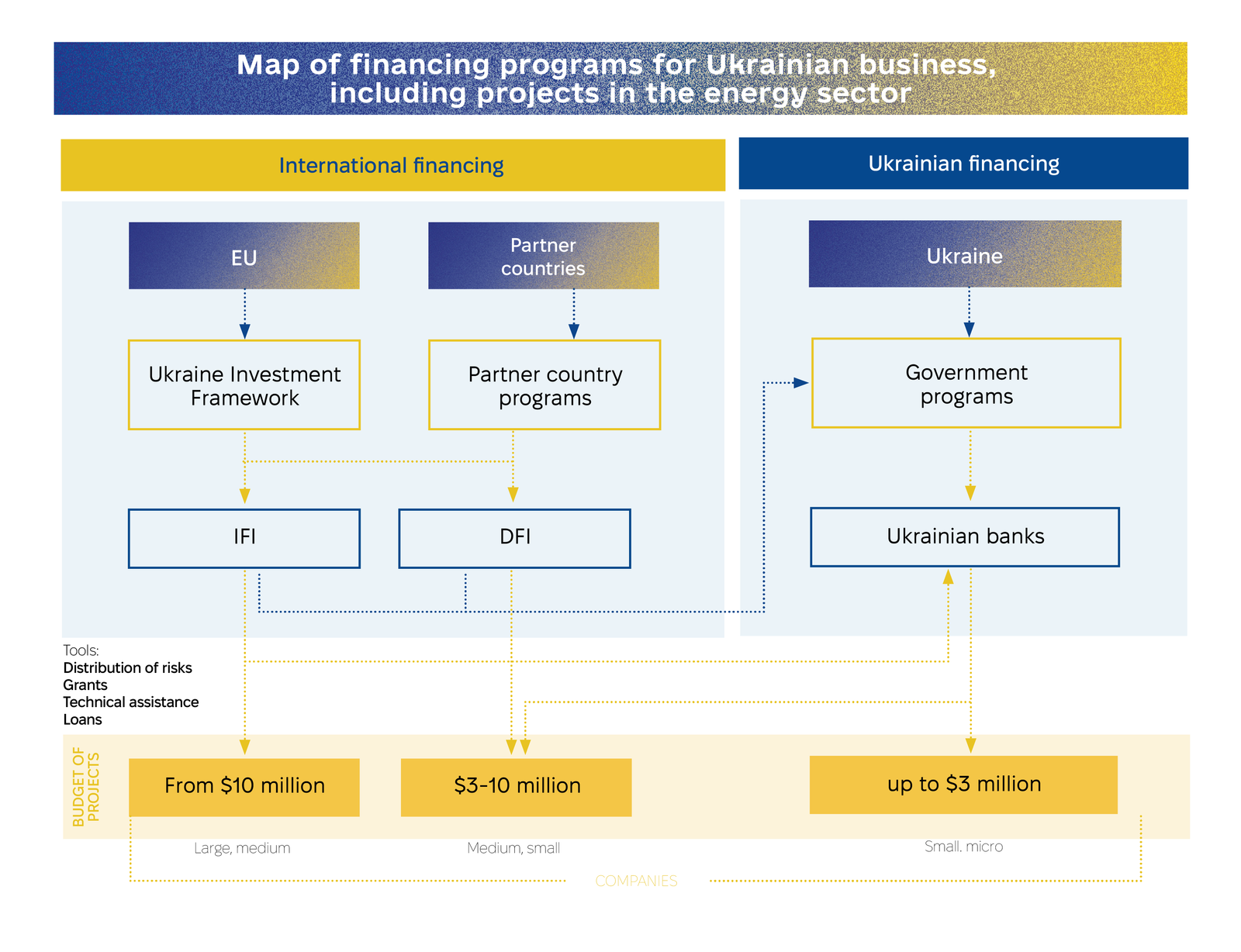
These efforts prioritize renewable energy development and infrastructure rehabilitation, creating a robust foundation for sustainable growth. By leveraging international funding mechanisms and domestic financial instruments, Ukraine is strengthening its energy resilience and driving progress in its transition to a green and modern energy system.
EFI funding programs and project areas
Under Phase 1 of the Ukraine Investment Framework (UIF), €1.4 billion in financing is available to Ukrainian companies through five Eligible Financial Institutions (EFIs), including the EIB, EBRD, IFC, KfW, and BGK. These funds are primarily directed at energy sector projects and are provided through guarantees, grants for mixed financing, and technical assistance. These financial products, implemented via Ukrainian banks, can be combined with domestic programs like the 5-7-9 initiative, offering more favourable conditions for companies seeking funding. Projects with budgets exceeding $10 million can also access direct financing from these EFIs.
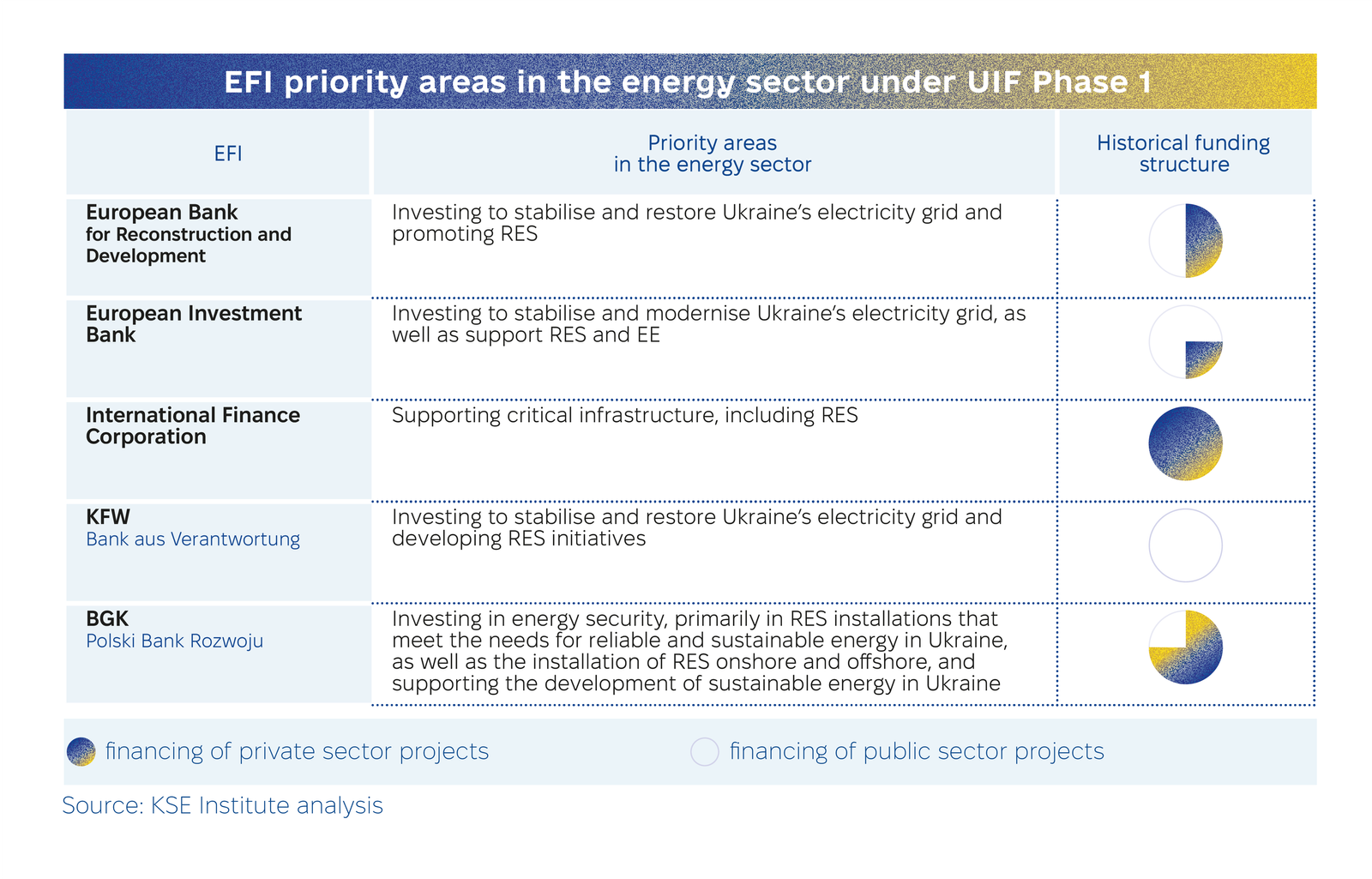
The energy sector is a key priority for all EFIs involved, with financing available for both public and private sector initiatives. By leveraging programs from Ukrainian banks alongside UIF support, up to €1.7 billion in funding could be accumulated in the coming years. While EFI requirements for borrowers overlap with those of Ukrainian banks, they also include unique conditions, enabling broader access to direct lending for sustainable development and energy sector growth.
Financing programs from Ukrainian banks
In June 2024, with the support of the National Bank of Ukraine (NBU), 20 leading banks representing over 85% of the sector’s net assets signed a Memorandum on Bank Lending for Energy Infrastructure Rehabilitation Projects. These financing programs cover a range of initiatives, including the construction of renewable energy facilities such as solar, wind, and biogas power plants, as well as energy-saving projects for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs). Between June and October 2024, banks received nearly 3,000 applications totalling UAH 66.2 billion, with UAH 11.7 billion already approved for infrastructure restoration projects.
Ukrainian banks offer tailored financing programs for the energy sector, often combined with instruments from the Ukraine Investment Framework (UIF), such as guarantees and blended finance, to provide more favourable conditions. Programs target SMEs, commercial businesses, and homeowners’ associations, with general eligibility criteria including profitability, compliance with ESG standards, and sound financial ratios. These initiatives are key to accelerating energy sector recovery and fostering sustainable growth for Ukrainian businesses.
DFIs financing projects
Development finance institutions (DFIs) play a critical role in supporting Ukraine’s economic development by providing funding for projects that promote sustainability and climate resilience. These institutions, financed by governments, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and EFIs, often prioritize renewable energy (RES) and energy efficiency (EE) initiatives. Many European DFIs are eligible to access the €9.3 billion UIF program of the European Commission, enabling them to implement impactful projects in Ukraine and further drive the country’s sustainable recovery.
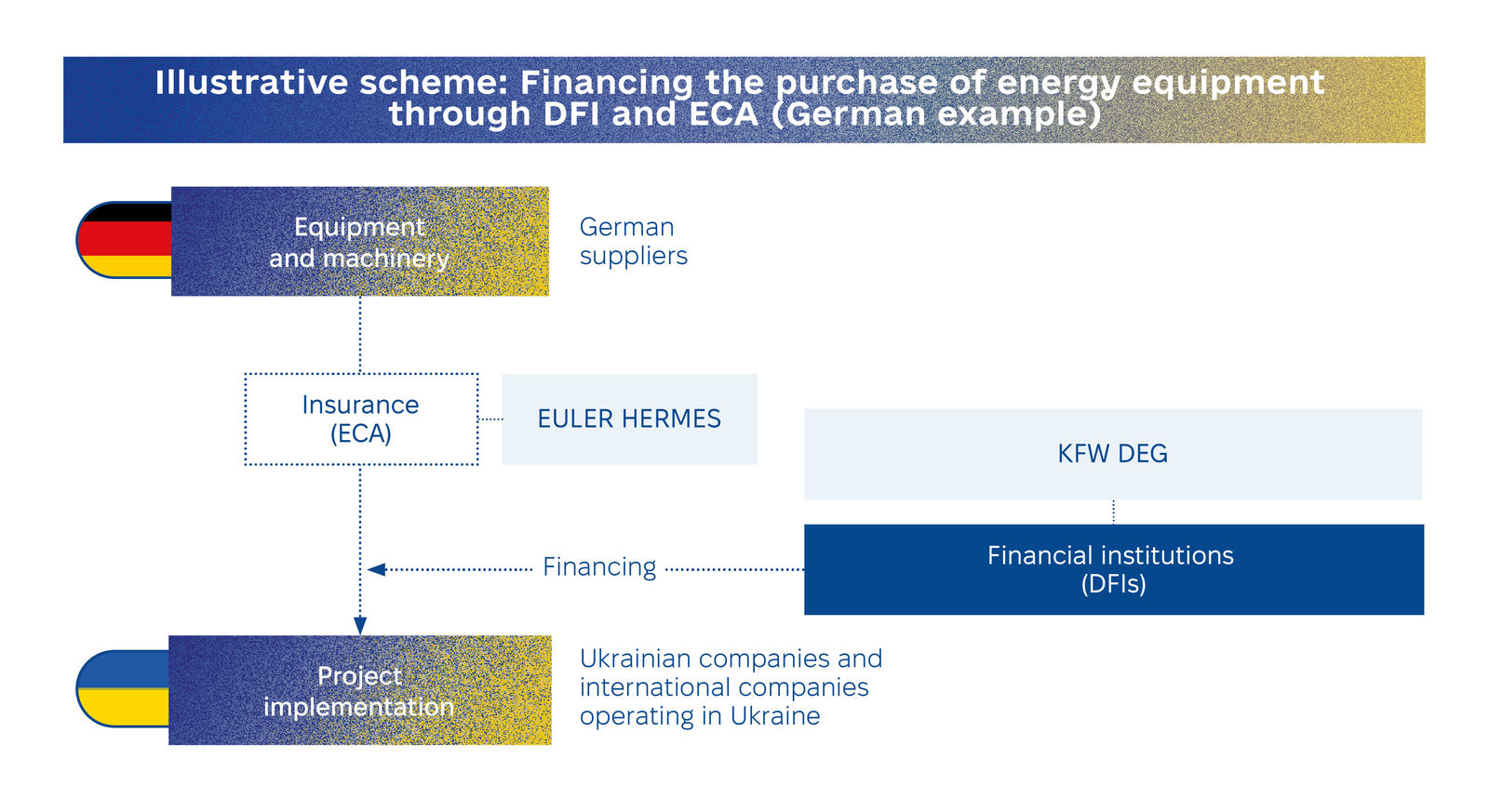
International and local financial institutions are ready to actively engage with private companies in Ukraine that are interested in implementing energy projects and provide financing to support the functioning of the energy system and the development of new energy initiatives. Projects financed through financial institutions must meet bankability requirements and have a measurable positive impact.
Additional requirements for projects may include:
- creation of new jobs
- increase in tax revenues
- providing net benefits to the environment
- promoting local infrastructure development and positive changes in the energy sector.
At the onset of the full-scale war, the National Bank of Ukraine (NBU) fixed the hryvnia exchange rate and imposed currency restrictions to stabilise the financial system and support businesses and households. Many restrictions are being lifted or amended as part of the NBU’s strategy to increase exchange rate flexibility and return to inflation targeting, contingent on economic conditions. This includes potentially allowing foreigners to transfer dividends abroad, influenced by inflation, reserve levels, and interest rates. The NBU’s measures align with IMF benchmarks, focusing on minimising exchange rate disparities and enhancing business trade and investment opportunities.
Ukraine has secured significant financial support to sustain its economy, including a USD 15.6 billion IMF Extended Fund Facility and a €50 billion Ukraine Facility programme from the European Union, aimed at budget support and investment in priority sectors.
Concurrently, Ukraine is advancing reforms to enhance its business environment and align with EU standards, crucial for accessing full financial support. Key reforms include business deregulation and public procurement alignment with EU standards, with 60% of the planned 156 reforms expected to be implemented by 2024.
-
Key Steps in the Financing Process
Key Steps in the Financing Process
Financing for energy projects typically involves direct funding for large-scale initiatives or intermediary funding for smaller projects via Ukrainian banks. The process follows three main stages: concept review, business plan evaluation, and final approval, with timelines varying based on project complexity and funding source.
- Two financing options: project-based (evaluated on performance) and corporate-based (evaluated on company metrics).
- Large projects (over $20 million) often funded by IFIs; smaller projects handled by Ukrainian banks.
- Timelines for financing range from a few months to a year.
Once the basic compliance requirements have been met, the decision-making process typically consists of three main stages.

-
Requirements for Investment Proposals
Requirements for Investment Proposals
Investment proposals must demonstrate profitability, environmental compliance, and alignment with energy sector goals. They should include clear financial structures, technical feasibility, and risk mitigation strategies to attract funding.
- Must meet financial, environmental, and energy security standards.
- Include market demand, project profitability, and technical soundness.
- Demonstrate strong organizational capacity and clear implementation plans.
- Proposals should address risks, infrastructure impacts, and regulatory compliance.
-
Recommended Steps for Feasibility Studies
Recommended Steps for Feasibility Studies
A well-prepared feasibility study (FS) is essential for securing funding, detailing project goals, technical approaches, market viability, and financial performance while addressing risks and regulatory requirements.
- Project Summary: Objectives, outcomes, financial indicators (NPV, IRR), and timelines.
- Project Description: Background, rationale, location, infrastructure, and stakeholder roles.
- Market Analysis: Size, competition, growth opportunities, and demand forecasts.
- Legal Framework: Permits, regulatory requirements, and legal risk assessment.
- Technical Design: Equipment, site suitability, performance metrics, and grid connection details.
- Financial Analysis: CapEx, OpEx, funding sources, ROI, and sensitivity analysis.
- Economic and Social Impact: Jobs created, community benefits, and CBA analysis.
- Environmental Impact: Compliance with IFI standards, sustainability plans, and biodiversity considerations.
- Risk Assessment: Identification of financial, technical, market, and environmental risks with mitigation plans.
Implementation Plan: Milestones, procurement strategy, and performance monitoring with KPIs.
 To learn more about the practical recommendations for preparing investment projects, download the full text of the chapter.Download Chapter
To learn more about the practical recommendations for preparing investment projects, download the full text of the chapter.Download Chapter
Between August 2023 and November 2024, Ukraine identified 326 energy projects worth over $65 billion, focusing on renewables, nuclear power, and energy infrastructure. Highlighting nine high-readiness projects totaling $7.7 billion, these initiatives aim to reduce emissions, enhance energy independence, and build a sustainable, competitive energy system.
Between August 2023 and November 2024, the KSE team, in partnership with the Ministry of Economy of Ukraine, compiled 326 energy sector investment projects with a total budget exceeding $65 billion. These initiatives span electricity generation and distribution, with the largest investments allocated to nuclear power plants (NPPs) at $20.3 billion, wind power plants (WPPs) at $17.8 billion, and electricity transmission infrastructure at $13.1 billion. Additional efforts include passive energy protection projects and decarbonization initiatives, reflecting Ukraine’s commitment to sustainable development and climate goals.
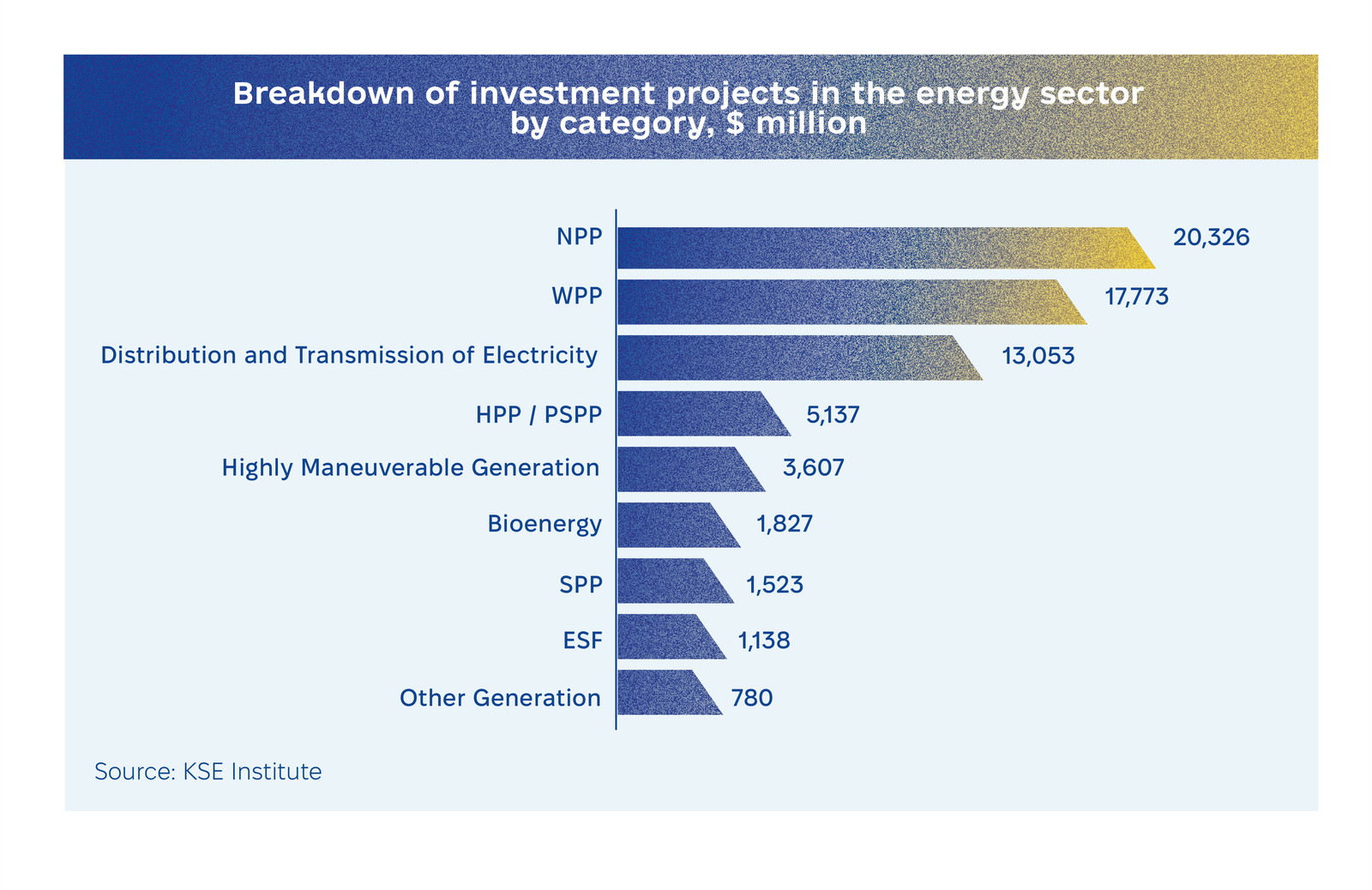
A significant share of the investment portfolio is concentrated in renewable energy, featuring 42 projects worth $4.4 billion, and two pumped storage power plant (PSPP) projects valued at $2.8 billion. These projects are critical for balancing renewable energy fluctuations, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting Ukraine’s green transition. By enhancing energy independence and competitiveness, they position Ukraine to export green energy resources to the EU and meet growing global climate policy demands.
In this chapter of the Energy Investment Guide, we also highlight nine high-readiness projects across various energy domains, including wind, solar, biomethane, and distributed gas generation. Together, these initiatives represent $7.7 billion in investments, with $6.4 billion requiring external financing. These projects embody Ukraine’s vision for a modernized, resilient, and sustainable energy system.
Access all materials and documents on Ukraine’s economy in our Digital Library.

